|
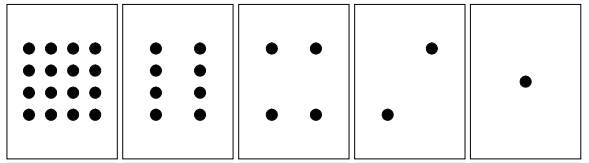
Today we learned how to count in binary using cards with dots on them.
1 Comment
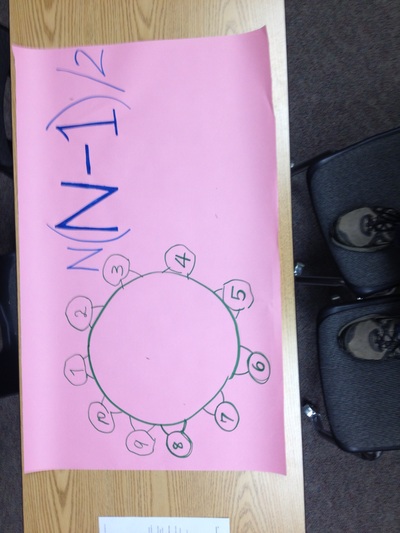
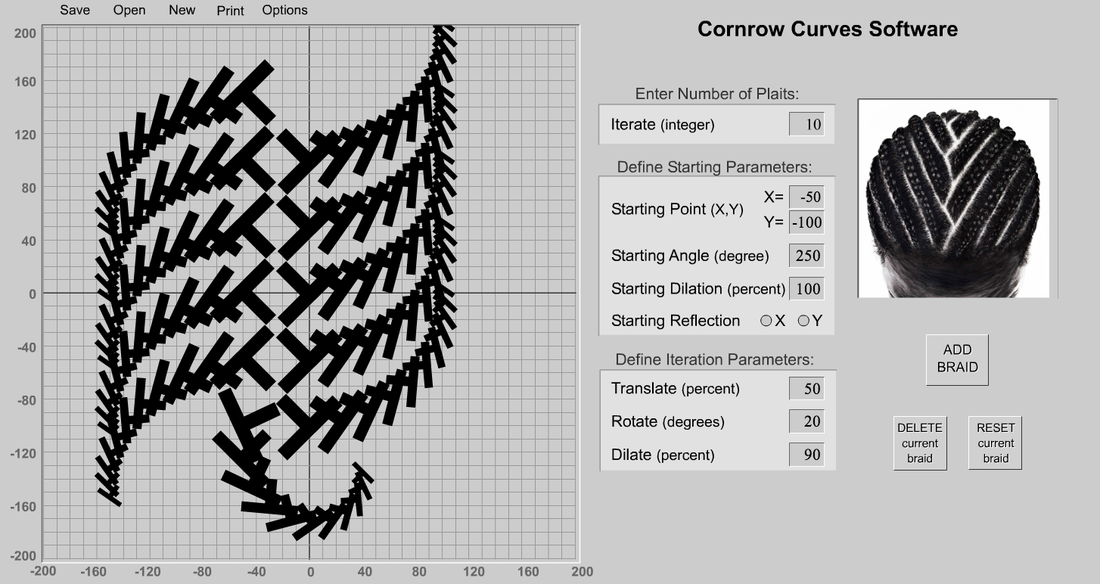
Today we had a problem to solve. We needed to design a new cornrow hair style for Lebron James for his first game as a new Cleveland Cavalier. But we first had to study about what cornrows are and the historical significance of the culture of cornrows and how to apply the patterns. We found that cornrows are rich with symbolism and the origins of cornrow hair styles go deep into African culture. (read about it here: http://csdt.rpi.edu/african/CORNROW_CURVES/culture/african.origins.htm)
We used the software from http://csdt.rpi.edu/african/CORNROW_CURVES/cornrow_software/cornrow_software.html to plan and implement our designs for Lebron's new hair style. Here is one example: Today we practiced using the problem solving process:
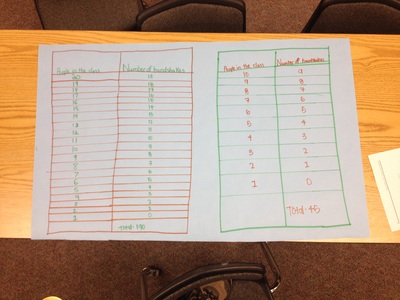
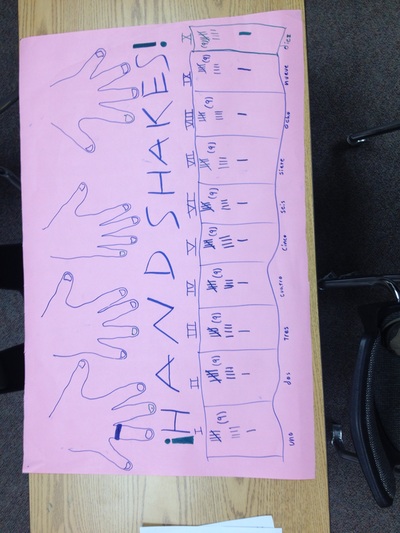
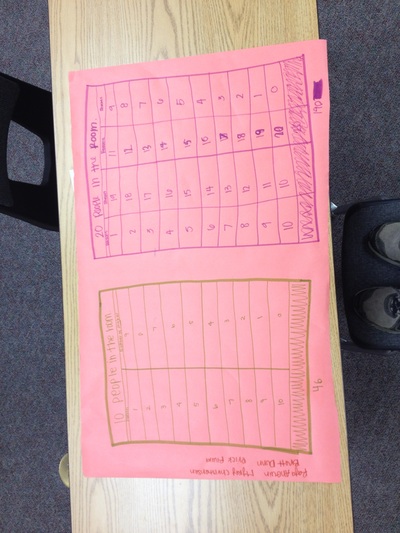
We solved the Handshake problem. Where we had to find out how many handshakes there would be if there were 10 people in the room and each person shook hands with each other person exactly once. Then we generalized it for any number of people in the room. We made plans and illustrated our solution on poster paper.  Today we learned the steps for the problem solving process: 1. Understand the problem 2. Plan the solution 3. Carry out the plan 4. Review and discuss your solution We practiced solve a few simple problems. We had the problem of breaking the candybar into 12 equal pieces, and shaking hands with each person in the room, and building a fence. We were in groups and we followed the steps for solving the problem. For some reason there were no trace of the candy bars at the end of the lesson. Data Collection Today we discussed the data that we give off as individuals. We wrote in our journals about the information that we give to people everyday. People thought of ideas like what we write on facebook or twitter, things we say when we talk to people, the texts we write, attendance at school, the homework we do, the papers we write, what we purchase at restaurants, what we search for on the internet, what we purchase on the internet, the books we check out from the library, how far we drive or walk, statistics of what happens in the games we play (i.e. number of sacks in a football game), the people we talk to, etc. All these things tell a story about our lives. Then we read a few articles online to help us think about how important our data is: http://www.nytimes.com/2006/08/09/technology/09aol.html http://blog.netflix.com/2010/03/this-is-neil-hunt-chief-product-officer.html http://www.nytimes.com/2010/03/17/technology/17privacy.html We discussed the articles and talked about our privacy and how the everyday data that we give off tells a very detailed story of who we are, and that is not something that is appropriate to be publicized. We agreed that good things can be done with our data, like a custom experience at a store, but for the most part it is best to keep that data private. We also brainstormed ideas of the data we would collect to solve the problem of installing a more useful public transportation solution (more public busses, bus routes, and bus stops). We figured out that collecting data through survey and population records would help us make the best decisions in planning bus routes and stops. |
Mr. AlveyThe host of the show disclosureArchives
November 2014
Categories
All
|
||||||||||||||||||||||






 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
